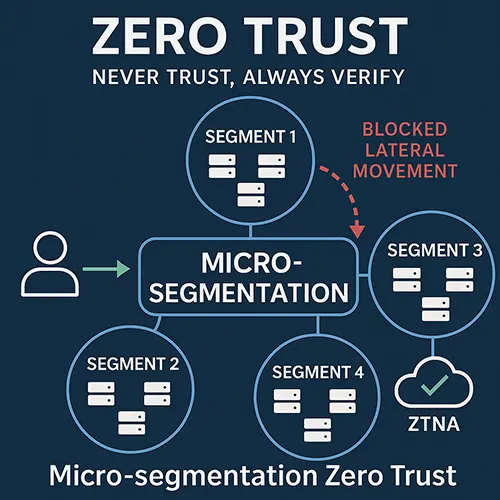
Why Micro-segmentation Zero Trust Matters
What is Micro-segmentation in Zero Trust?
Micro-segmentation is the practice of dividing networks into isolated zones and applying fine grained security policies to control traffic between them. In a Zero Trust context, it goes further:
access between these segments is granted only after verifying identity, device posture, and context.
Unlike traditional segmentation, which relies on firewalls and VLANs, micro-segmentation Zero Trust operates at the workload level, leveraging identity and dynamic policies. This ensures that trust is never implicit; every interaction must be validated.
Why Micro-segmentation is Core to Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust architecture (ZTA) aims to eliminate the assumption of trust within internal networks.
Micro-segmentation supports this by:
- Limiting lateral movement: Attackers cannot move freely once inside.
- Enhancing visibility: Security teams gain granular insights into east-west traffic.
- Supporting least privilege: Policies enforce access only where necessary.
- Protecting sensitive workloads: Finance, HR, or healthcare data are isolated from less secure zones.


How Micro-segmentation Works in Zero Trust
Implementing micro-segmentation involves more than just dividing the network.
In Zero Trust, it operates on identity and context-driven policies.
- Identify assets: Map applications, workloads, and data flows.
- Define policies: Allow or deny traffic based on identity, not just IP addresses.
- Enforce dynamically: Policies adapt to workload changes in hybrid or cloud environments.
- Monitor continuously: Use SIEM & Analytics to validate traffic and detect anomalies. Continuous monitoring is typically powered by SIEM & Analytics, which not only collect logs but also detect suspicious patterns and potential attacks.
Integration with IAM and MFA
Micro-segmentation delivers the highest value when integrated with Identity & Access Management (IAM) systems. This ensures that access decisions are enforced based on user identity and roles. In addition, adopting Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) strengthens security by verifying that only legitimate users can reach sensitive network segments.
Benefits of Micro-segmentation in Zero Trust
- Reduced attack surface: Each segment is isolated, minimizing risk.
- Improved compliance: Easier to meet standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
- Granular control: Identity-driven policies, not just network location.
- Visibility and monitoring: Full insight into workload communications.
Challenges of Implementing Micro-segmentation
While powerful, micro-segmentation is not without challenges:
- Complexity: Mapping traffic flows and dependencies can be difficult.
- Operational overhead: Requires continuous monitoring and policy updates.
- Tool selection: Choosing between VMware NSX, Cisco Tetration, Illumio, and others.
- Risk of misconfiguration: Poorly designed policies can block legitimate traffic.
Tools and Platforms for Zero Trust Micro-segmentation
Several leading platforms enable micro-segmentation within Zero Trust:
- VMware NSX – Advanced policy enforcement across hybrid environments.
- Cisco Secure Workload (Tetration) – Strong analytics and policy modeling.
- Illumio – Agent-based micro-segmentation with real-time visibility.
- Guardicore (by Akamai) – Focus on software-defined segmentation and breach containment.
Micro-segmentation vs. Network Segmentation
Complementing Firewalls & Endpoint Security
While micro-segmentation enforces policies at the workload and identity level, it works best in synergy with Firewalls & Endpoint Security. Firewalls serve as the first line of defense, while micro-segmentation provides deeper, more granular protection inside the network.
| Aspect | Network Segmentation | Micro-segmentation Zero Trust |
|---|---|---|
| Granularity | Per VLAN / subnet | Per workload / application |
| Policy basis | IP address / location | Identity, device, context |
| Visibility | Limited (north-south traffic) | Full (east-west traffic) |
| Zero Trust alignment | Partial | Native |
Real-world Use Cases
- Data centers: Isolate critical databases from less secure workloads.
- Cloud-native apps: Secure Kubernetes pods and microservices.
- Hybrid environments: Apply consistent policies across on-premises and cloud.
Best Practices for Implementing Micro-segmentation Zero Trust
- Start small: Pilot with a critical application.
- Leverage visibility tools: Map flows before enforcing policies.
- Integrate with IAM and SIEM: Ensure policies are identity- and context-driven.
- Automate where possible: Use orchestration to reduce human error.
- Review regularly: Update policies as applications and threats evolve.